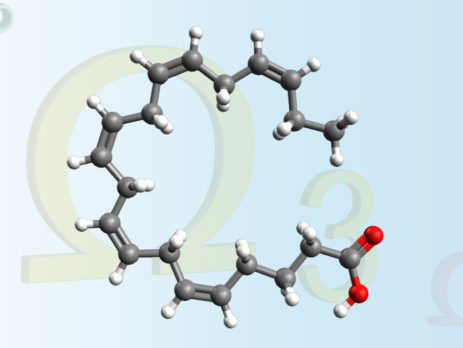
Astaxanthin
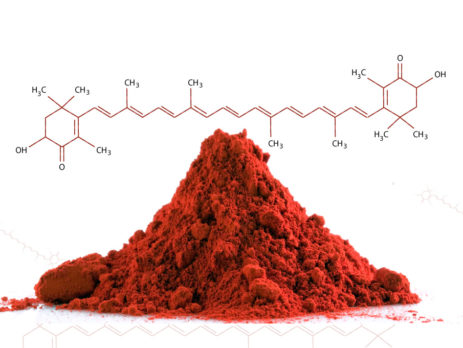
Astaxanthin is a carotenoid naturally present in some algae (Haematococcus pluvialis) and which gives their typical color to fish such as salmon and crustaceans such as lobster, shrimp and Krill. It is endowed with antioxidant power: it is therefore attributed the ability to protect cells from damage associated with oxidation. It is also believed to improve the functioning of the immune system. Its intake is proposed in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's, stroke, high cholesterol and age-related macular degeneration....